 Last updated: September 29th, 2023 4:03 PM
Last updated: September 29th, 2023 4:03 PM
Professional Tax Registration and Compliance
Professional tax is a direct tax levied on persons earning an income by either practicing a profession, employment, calling, or trade. Unlike income tax imposed by the Central Government, professional tax is levied by the government of a state or union territory in India. In the case of salaried and wage earners, the professional tax is liable to be deducted by the Employer from the salary/wages, and the same is to be deposited to the state government. In the case of other classes of individuals, this tax is liable to be paid by the employee himself. The tax calculation and amount collected may vary from one State to another, but it has a maximum limit of Rs. 2500/- per year. The present article briefs the Professional Tax Registration in detail.Professional Tax Applicability
This tax is levied on all kinds of professions, trades, and employment. Profession tax is applicable to the following classes of persons:- An Individual
- A Hindu Undivided Family (HUF)
- A Company/Firm/Co-operative Society/Association of persons or a body of individuals, whether incorporated or not
Professional Tax Applicable States across India
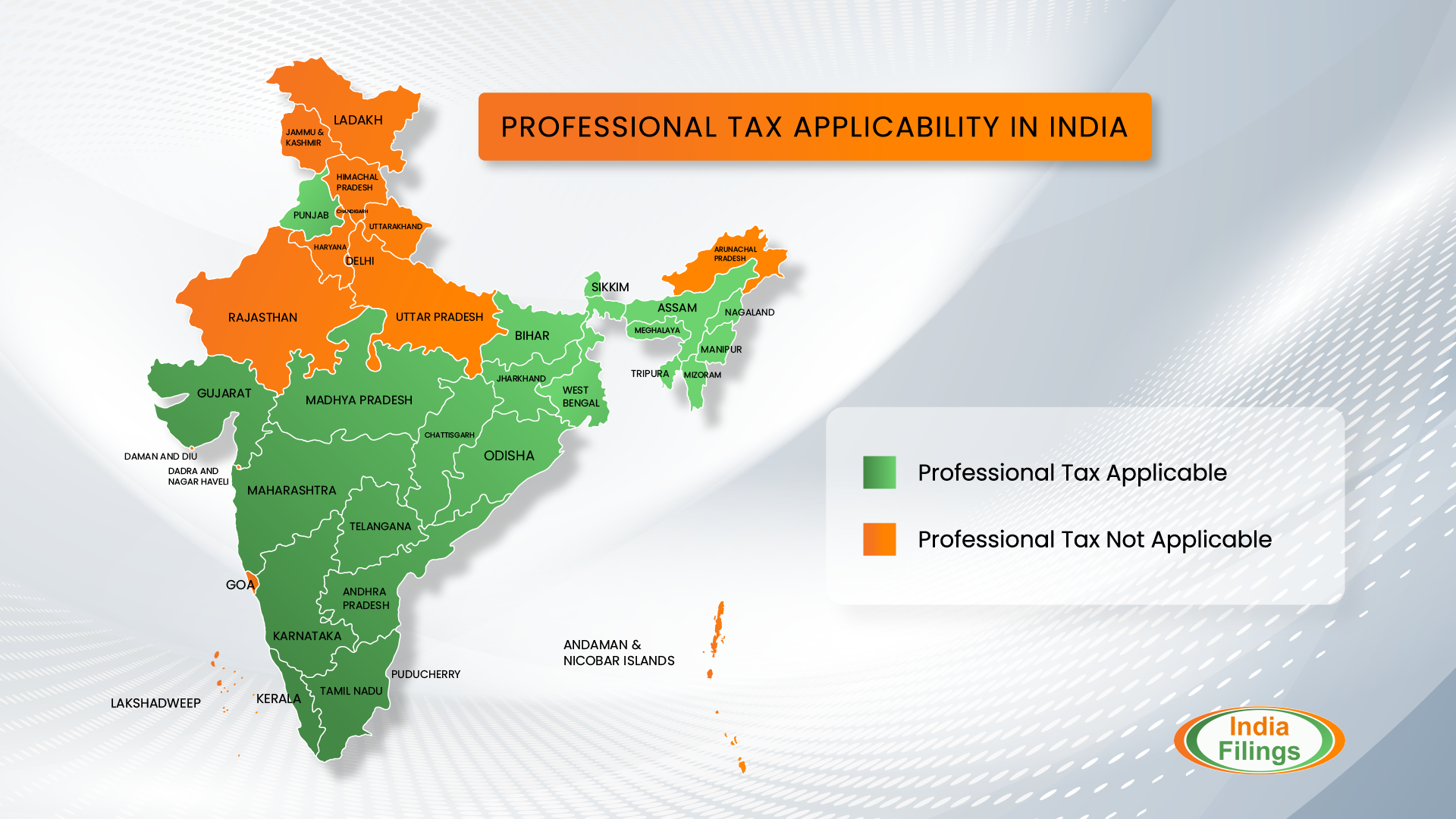 Professional Tax Applicable States across India
Please refer to the following table to know more about the states which impose professional tax in India:
Professional Tax Applicable States across India
Please refer to the following table to know more about the states which impose professional tax in India:
| Applicable States | Non-Applicable States |
| Andhra Pradesh Assam Bihar Gujarat Jharkhand Karnataka Kerala Madhya Pradesh Maharashtra Manipur Meghalaya Mizoram Nagaland Odisha Pondicherry Punjab Sikkim Tamil Nadu Telangana Tripura West Bengal | Central Andaman and Nicobar Islands Arunachal Pradesh Chandigarh Chhattisgarh Dadra and Nagar Haveli Daman and Diu Delhi Goa Haryana Himachal Pradesh Jammu and Kashmir Ladakh Lakshadweep Rajasthan Uttar Pradesh Uttarakhand |
Professional Tax Rate
The maximum amount payable per annum towards professional tax is INR 2,500. The professional tax is usually a slab amount based on the gross income of the professional. It is deducted from his income every month. The Commercial Taxes Department of a state/union territory is the nodal agency that collects professional tax on the basis of predetermined tax slabs which vary for each state and union territory. The tax is calculated on the annual taxable income of the individual; however, it can be paid either annually or monthly.Profession Tax Rates in the Key States of India
As this tax is a state subject, the rate of professional tax varies from one State to another. While some states might charge it as a percentage value, other states tend to charge it as a fixed amount based on income slabs. The following are the professional tax rates in key states in India:| State | Income per Month | Tax Rate/Tax Amount (Per Month) |
| Andhra Pradesh | Less than Rs. 15,000 | Nil |
| Rs. 15,000 to less than Rs. 20,000 | Rs. 150 | |
| Rs. 20,000 and above | Rs. 200 | |
| Gujarat | Up to Rs. 5999 | Nil |
| Rs. 6000 to Rs. 8999 | Rs. 80 | |
| Rs. 9000 to Rs. 11999 | Rs. 150 | |
| Rs 12000 and above | Rs. 200 | |
| Karnataka | Up to Rs. 15,000 | Nil |
| Rs. 15,001 onwards | Rs. 200 | |
| Kerala (Half yearly income slabs and half-yearly tax payment) | Up to Rs.11,999 | Nil |
| Rs.12,000 to Rs.17,999 | Rs.120 | |
| Rs.18,000 to Rs. 29,999 | Rs.180 | |
| Rs.30,000 to Rs. 44,999 | Rs.300 | |
| Rs.45,000 to Rs. 59,999 | Rs.450 | |
| Rs.60,000 to Rs. 74,999 | Rs.600 | |
| Rs.75,000 to Rs. 99,999 | Rs.750 | |
| Rs.1,00,000 to Rs. 1,24,999 | Rs.1000 | |
| Rs.1,25,000 onwards | Rs.1250 | |
| Maharashtra | Up to Rs. 7,500 | Nil (for male) |
| Up to Rs. 10,000 | Nil (for female) | |
| From Rs. 7,500 to Rs. 10,000 | Rs. 175 (for males) | |
| Rs. 10,000 onwards | Rs. 200 for 11 months + Rs. 300 for 12th month | |
| Telangana | Up to Rs. 15,000 | Nil |
| Rs.15,001 to Rs.20,000 | Rs. 150 | |
| Rs.20,001 onwards | Rs.200 | |
| Up to 5 years (For professionals such as legal practitioners, CA, architects, etc.) | Nil | |
| Over 5 years (For professionals such as legal practitioners, CA, architects, etc.) | Rs. 2,500 (per annum) | |
| West Bengal | Up to 10,000 | Nil |
| 10,001 to 15,000 | Rs. 110 | |
| 15,001 to 25,000 | Rs. 130 | |
| 25,001 to 40,000 | Rs. 150 | |
| 40,001 and above | Rs. 200 |
Profession Tax Is Deductible under Section 16 (iii) Of The Income Tax Act
According to Section 16 (iii) of the Income Tax Act 1961, the professional tax paid by an employee is allowed as a deduction from his/her gross salary income.Who Pays Profession Tax?
In the case of Salaried and Wage-earners, the Professional Tax is liable to be deducted by the Employer from the Salary/Wages, and the Employer is liable to deposit the same with the state government Self-employed persons who carry out their profession or trade on their own and fall in the ambit of profession tax are liable to pay the tax themselves to the state government.Employer’s Responsibility for Professional Tax
The owner of a business is responsible for deducting professional tax from the salaries of his employees and paying the amount so collected to the appropriate government department. He/she has to furnish a return to the tax department in the prescribed form within the specified time. The return should include proof of tax payment. In case of not enclosing the payment proof, the register will consider the return incomplete and invalid.Exemptions for Payment of Professional Tax
There are exemptions provided for certain individuals to pay Professional Tax under the Professional Tax Rules. The following individuals are exempted to pay Professional Tax:- Parents of children with permanent disability or mental disability
- Members of the forces as defined in the Army Act, 1950, the Air Force Act, 1950, and the Navy Act, 1957 including members of auxiliary forces or reservists, serving in the State.
- Badli workers in the textile industry
- An individual suffering from a permanent physical disability (including blindness)
- Women exclusively engaged as agents under the Mahila Pradhan Kshetriya Bachat Yojana or Director of Small Savings.
- Parents or guardians of individuals suffering from a mental disability.
- Individuals, above 65 years of age
Professional Tax Registration and Compliance
Professional Tax Registration is mandatory within 30 days of employing staff in a business or, in the case of professionals, 30 days from the start of the practice.- Application for the Registration Certificate should be made to the assessed state tax department within 30 days of employing staff for his business.
- If the assessee has more than one place of work, then the application should be made separately to each authority with respect to the place of work under the jurisdiction of that authority.
Due Dates for Professional Tax Payment
If an employer has employed more than 20 employees, he is required to make the payment within 15 days from the end of the month. However, if an employer has less than 20 employees, he is required to pay quarterly (i.e. by the 15th of next month from the end of the quarter).Professional Tax Return
The Professional Tax Return is to be filed by all the persons having Professional Tax Registration and the due dates for filing of such returns vary from State to State.
Benefits of Professional Tax Registration
The benefits of Professional tax Registration are given below:- It is simple to comply with the Professional Tax Compliance, which results in a smooth registration process with minimum restrictions.
- It is compulsory to pay Professional tax as per the law. Hence, the timely payment of Professional tax can help avoid penalties and any punitive action against the Employer or a self-employed person.
- Professional Tax Compliance is simple, which can enable a smooth and hassle-free Registration Process.
- The Professional Tax acts as a revenue source for the state governments that helps the government to implement schemes for the various welfare and development of the region.
- The Employer or the self-employed person can claim a deduction on the previously paid professional tax.
Documents required for Professional Tax Registration
- Certificate of Incorporation / LLP Agreement
- MOA and AOA
- PAN Card of Company/LLP/Proprietor/Owner/Director
- NOC from the landlord, where the business is situated
- Passport size photos of Proprietor/Owner/Director
- Address and identity proof of Proprietor/Owner/Director
- Details of employees and salaries paid
- Additional registrations and licenses
Procedure for Professional Tax Registration
The procedure for Professional Tax Registration depends from State to State. Further, Returns must also be filed at specified intervals depending on the State’s requirement. Professionals /Employers seeking professional tax registration shall follow the below-mentioned procedure.- The applicant must file the application form and the requisite documents.
- The applicant needs to submit the Application with the necessary documents to the concerned state government. A copy of the same should also be submitted to the tax department.
- On receipt of an application, the tax authority shall scrutinize the application to ensure that all the information is correct.
- Issue of Registration Certificate: The authority will issue the Registration certificate after successfully scrutinizing all the documents.
Penalties Related To Professional Tax Registration
When professional tax policy becomes applicable, all such jurisdictions may impose a penalty for failure to register Profession Tax. However, the precise amount of the Penalty will depend on state regulatory law. There are also penalties for failing to submit the PT return by the deadline and withholding payments after they are due. Each state's professional tax regulations determine the actual fine. Businesses that fail to register professional tax, pay taxes late, or file returns on time may face fines, late fees, or imprisonment. Failure to make a payment by the due date and failure to file a return by the due date carries additional penalties. For example, the following information outlines the penalty amount imposed by the Maharashtra Government for late filing or failure to pay Professional Tax in Maharashtra.| Nature of default | Penalty Leviable |
| Not obtaining PT registration | Rs.5/- per day |
| Late filing of PT return | Rs.1,000/- |
| Late payment of PT dues | Interest @1.25% p.m. Penalty @10% |
Popular Post

In the digital age, the convenience of accessing important documents online has become a necessity...

The Atalji Janasnehi Kendra Project that has been launched by the Government of Karnataka...

The Indian Divorce Act governs divorce among the Christian couples in India. Divorce...

When an individual has more than a single PAN card, it may lead to that person being heavily penalised, or worse,...

Employees Provident Fund (PF) is social security and savings scheme for employee in India. Employers engaged...


