 Last updated: November 27th, 2024 12:37 PM
Last updated: November 27th, 2024 12:37 PM
TDS on Salary under Section 192 - Rates, Forms, & Calculation
TDS (Tax Deduction at Source) on Salary is the amount deducted from an employee's income at the source by an authorized deductor and deposited to the Income tax department. Section 192 is synonymous with the TDS on salary section. It outlines guidelines for employers to deduct the TDS from the salary of an employee before an actual payment. Calculating TDS under Section 192 involves considering your gross salary, applicable TDS deduction on salary and exemptions, and arriving at an estimated tax amount. This article gives comprehensive information regarding the salary TDS section, what is TDS in salary, rates, how to calculate it, TDS on salary limit, and forms.
IndiaFilings streamlines your TDS return filing with expert assistance! [shortcode_35]What is Tax Deduction at Source (TDS)?
TDS, or "Tax Deduction at Source", involves the deduction and remittance of income tax by the person paying the income. The person deducting the tax is known as "Tax Deductor", the person from whom the tax is deducted at source is called "Tax Deductee". TDS is usually required on the following transactions:
- Salary payments
- Interest on securities
- Dividend payments
- Interest other than interest on securities
- Winning from Lottery or Crossword Puzzle
- Winning from Race Horse
- Payment to Contractor and Sub-Contractors
- Insurance Commission
- Deposits under NSS
- Repurchase of Units by Mutual Fund or UTI
- Commission on the sale of Lottery Tickets
- Commission or Brokerage
- Rent
- Transfer of immovable property
- Fees for professional or technical services
- Income with respect to units
- Compensation on acquisition of immovable property
What is TDS in Salary?
To answer the question, what is TDS in salary, it is essentially means that a portion of your income tax is deducted by your employer when they pay your salary. This amount is then deposited with the government on your behalf. Before the deduction of TDS, the employer must first obtain TAN Registration. A TAN number, or Tax Deduction and Collection Account Number, is a 10-digit alphanumeric number used by the Income Tax Department to track all TDS deduction on salary and remittances. The employer will not deduct the TDS if it is below or on the specified TDS on salary limit.
Who deducts TDS on salary?
The responsibility to deduct the salary as per TDS rates falls upon every employer who pays a taxable salary to their employees, as per the salary TDS section. This includes:- Individuals
- Companies (Private and Public)
- Hindu Undivided Families (HUFs)
- Trusts (Societies, charitable institutions, etc.)
- Partnership firms
- Co-operative Societies
When is the TDS deducted from salary?
TDS is generally deducted when your salary is paid, regardless of whether it's early, on time, or late. This applies to both monthly and yearly salaries. However, there are exceptions. If your annual salary is below the basic exemption TDS on salary limit ( ₹2,50,000 for FY 2024-25), then no TDS will be deducted. Additionally, if you don't have a Permanent Account Number (PAN), TDS may be deducted at a higher rate of 20%.TDS rate on Salary
TDS deduction on salary is based on the income tax slab rates for the applicable financial year. Your deduction rates depend upon which tax regime you belong to. Below are the TDS rates chart on salary for both the old and new tax regimes. In the table below, we have given the TDS rate on Salary slab for the Old Tax RegimeFor Individuals Below 60 years:
| Income Slabs | TDS rate on salary |
| Up to ₹2.5 lakh | NIL |
| ₹2.5 lakh – ₹5 lakh | 5% |
| ₹5 lakh – ₹10 lakh | 20% |
| Above ₹10 lakh | 30% |
For Senior Citizens (Between 60-80 years of age):
| Income Slabs | TDS rate on salary |
| ₹0 – ₹3 lakh | NIL |
| ₹3 lakh – ₹5 lakh | 5% |
| ₹5 lakh – ₹10 lakh | 20% |
| Above ₹10 lakh | 30% |
For Super Seniors ( Above 80 years of age):
| Income Slabs | TDS rate on salary |
| ₹0 – ₹5 lakh | NIL |
| ₹5 lakh – ₹10 lakh | 20% |
| Above ₹10 lakh | 30% |
TDS rate on Salary for New Tax Regime
| Income Slab | TDS rate on salary |
| Upto ₹3,00,000 | Nil |
| ₹3,00,001 - ₹6,00,000 | 5% |
| ₹6,00,001 - ₹9,00,000 | 10% |
| ₹9,00,001 - ₹12,00,000 | 15% |
| ₹12,00,001 -₹15,00,000 | 20% |
| ₹15,00,000 and above | 30% |
How to Calculate TDS on Salary Section 192?
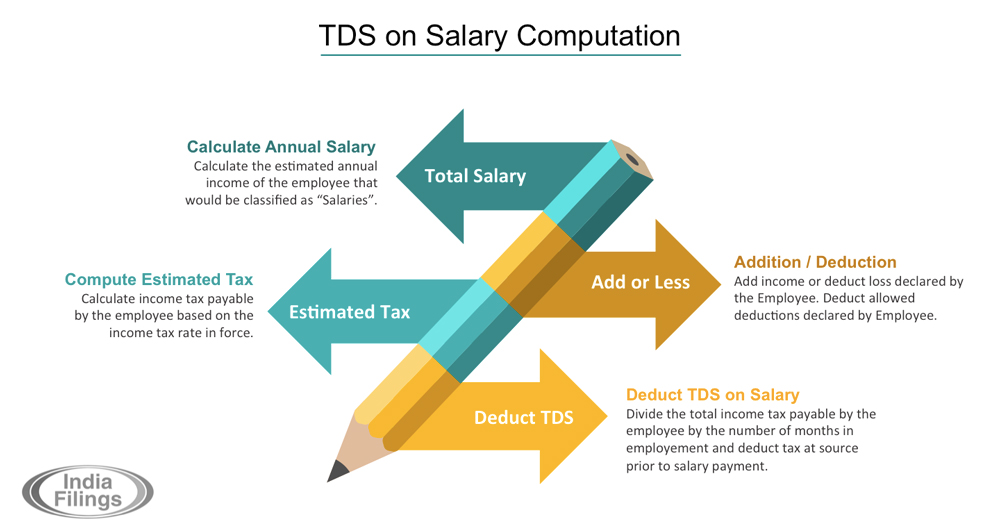 The following steps can be used by employers to calculate TDS on an employee’s salary,
Step 1: Estimate Employee's Annual Salary - The employer considers the employee's estimated salary for the entire financial year.
Step 2: Account for Exemptions - Exemptions under Section 10 of the Income Tax Act are factored in. These may include House Rent Allowance (HRA), Leave Travel Concession (LTC), etc. The employee must submit investment proofs or relevant documentation to claim these exemptions.
Step 3: Calculate Taxable Income - The estimated annual exemptions are subtracted from the gross annual salary to arrive at the taxable income amount.
Step 4: Determine Tax Rate - The applicable tax slab rate for the employee's taxable income is determined based on their income tax regime (old or new) and age.
Step 5: Calculate Annual Tax Liability - The tax rate is applied to the taxable income to determine the employee's estimated annual tax liability.
Step 6: Divide by Remaining Months - The annual tax liability is divided by the number of months remaining in the financial year for which TDS applies. This gives the monthly TDS amount the employer should deduct from the employee's salary. It will give the answer for how much TDS is deducted on salary per month.
Our IndiaFilings tax experts help you calculate the TDS amount accurately and file it on time.
The following steps can be used by employers to calculate TDS on an employee’s salary,
Step 1: Estimate Employee's Annual Salary - The employer considers the employee's estimated salary for the entire financial year.
Step 2: Account for Exemptions - Exemptions under Section 10 of the Income Tax Act are factored in. These may include House Rent Allowance (HRA), Leave Travel Concession (LTC), etc. The employee must submit investment proofs or relevant documentation to claim these exemptions.
Step 3: Calculate Taxable Income - The estimated annual exemptions are subtracted from the gross annual salary to arrive at the taxable income amount.
Step 4: Determine Tax Rate - The applicable tax slab rate for the employee's taxable income is determined based on their income tax regime (old or new) and age.
Step 5: Calculate Annual Tax Liability - The tax rate is applied to the taxable income to determine the employee's estimated annual tax liability.
Step 6: Divide by Remaining Months - The annual tax liability is divided by the number of months remaining in the financial year for which TDS applies. This gives the monthly TDS amount the employer should deduct from the employee's salary. It will give the answer for how much TDS is deducted on salary per month.
Our IndiaFilings tax experts help you calculate the TDS amount accurately and file it on time.
How much TDS is deducted on salary per month?
The amount of TDS deducted on salary per month depends on an individual’s total annual income, applicable income tax slabs, and eligible deductions under the Income Tax Act. Employers calculate the TDS based on the employee’s estimated annual taxable income and deduct it proportionally each month. As we detailed in the TDS calculation section, to determine how much TDS is deducted on salary per month, the employer considers factors such as exemptions (e.g., HRA, LTA), deductions (e.g., under Sections 80C, 80D), and any declared investments. Employees can request their employer to adjust the TDS by submitting proof of investments and eligible deductions during the financial year.Is it possible to claim back TDS?
Yes, you can claim back TDS (Tax Deducted at Source) if the amount deducted was more than your actual tax liability. This can happen for various reasons like claiming exemptions you weren't aware of earlier or not submitting investment proofs on time. To claim the refund, you must file your Income Tax Return (ITR) and accurately report your income and deductions. The Income Tax Department will process your return and initiate a refund if applicable. Also read: How to check ITR refund status?Forms for TDS on Salary
In the context of Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) on salary, the primary form involved is Form 24Q. Employers utilise this form to declare the TDS deducted from employee salaries to the government every quarter. Employees themselves generally do not need to complete any forms for salary-related TDS. However, they will receive Form 16 (TDS Certificate) after the financial year. This document details the total salary earned and the corresponding TDS deducted by the employer. Here’s the Form 24Q for your reference,Form No.16 - TDS Certificate
Below, we have given the format of Form No.16A (TDS Certificate) for your reference, Also read: Section 192A of the Income Tax ActNon-compliance for TDS on Salary Section
Suppose the employer has deducted TDS on Salary but not deposited it with the Government. In that case, the employee cannot be called to pay the tax himself, as the employer has defaulted in paying the tax deducted to the Government.
If the employer does not deduct TDS, the employee is liable to pay the Income Tax due as per salary TDS section. Further, when TDS is not deducted and remitted by the employer, the entire expenses relating to the salary payment are disallowed as an expenditure for the Employer, increasing the employer's income tax liability. Know more about income tax penalties.
Conclusion
This article provides a comprehensive guide to TDS (Tax Deducted at Source) on salary in India. It explains the concept, who deducts it, when it's deducted, and how it's calculated. The article also covers claiming TDS refunds, the relevant forms (Form 24Q for employers and Form 16 for employees), and the potential consequences of non-compliance for employers. Calculate and file the TDS returns effortlessly with IndiaFilings experts!! [shortcode_35]Popular Post

In the digital age, the convenience of accessing important documents online has become a necessity...

The Atalji Janasnehi Kendra Project that has been launched by the Government of Karnataka...

The Indian Divorce Act governs divorce among the Christian couples in India. Divorce...

When an individual has more than a single PAN card, it may lead to that person being heavily penalised, or worse,...

Employees Provident Fund (PF) is social security and savings scheme for employee in India. Employers engaged...


