 Updated on: October 3rd, 2023 5:05 PM
Updated on: October 3rd, 2023 5:05 PM
What is Professional tax?
When you're employed and receive a consistent salary, fulfilling your professional tax obligations becomes mandatory. You have likely encountered this term on your monthly salary slips or Form 16, listed beneath your gross salary, allowances, and HRA. Professional tax is one of the deductions from your gross salary, alongside TDS, EPF, and other applicable deductions. Contrary to common misconception, this tax isn't exclusively for professionals like doctors or lawyers; it applies to anyone earning a salary. Let's delve into the intricacies of professional tax to gain a better understanding. [shortcode_57]Professional Tax
Professional tax, a direct deduction from your gross salary facilitated by your employer, is a state government-imposed levy, making its rates subject to variation based on your place of residence within the country. The maximum cap on this tax is set at Rs 2500, with its computation being reliant on specific income slabs, which can differ from state to state.Who Must Pay Professional Tax?
Professional tax is not limited to specific professions; it applies to various individuals and entities. The following categories of persons and entities are subject to professional tax:- Companies and Business Firms
- Limited Liability Partnerships (LLPs)
- Corporations
- Co-operative Societies and Associations
- Hindu Undivided Families
- Clubs
- Lawyers and Legal Practitioners
- Contractors
- Architects
- Engineers
- Insurance Agents
- Chartered Accountants (CAs)
- Company Secretaries (CS)
- Surveyors
- Tax Consultants
- Management Consultants
- Doctors and Other Medical Representatives
Professional Tax Applicable States across India
Please refer to the following image to learn more about the states which impose professional tax in India: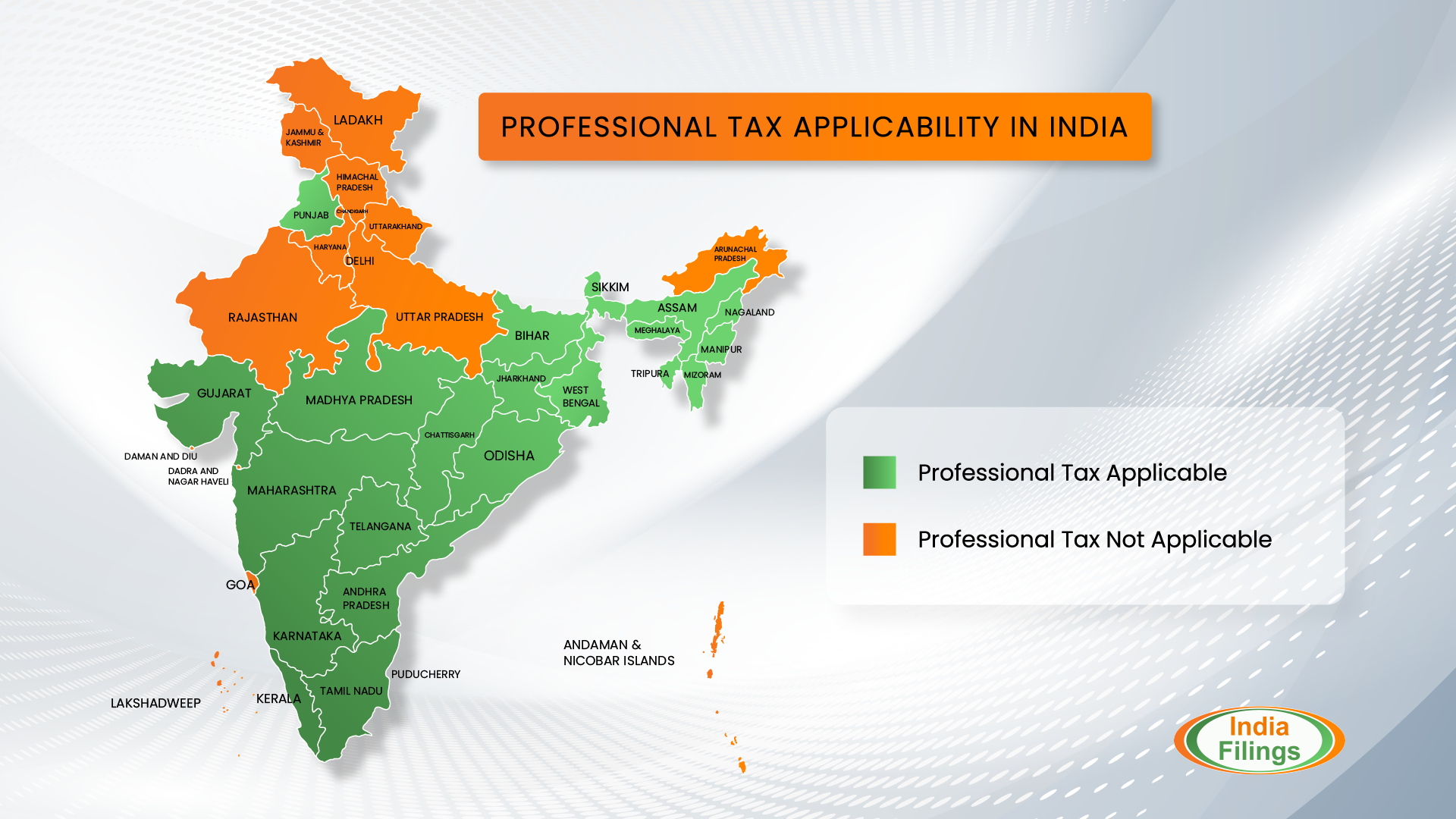
Understanding Professional Tax Rates in India
Professional tax rates in India vary from state to state, as each state government has the authority to enact its own laws and regulations governing this tax within its jurisdiction. Despite these regional variations, a commonality among states is adopting a slab system that determines the professional tax liability based on an individual's income. Professional Tax Slab Professional Tax is a state-specific tax in India, meaning the tax rates and slabs can differ from one state to another. Some states levy professional tax as a percentage of income, while others use a fixed amount based on income slabs to determine the tax liability. For more details on Professional Tax Slab, refer to 0ur articleMaximum Limit for Professional Tax
Article 276 of the Indian Constitution empowers state governments to levy professional tax and prescribes a maximum cap of Rs 2,500. No person can be charged a professional tax exceeding Rs 2,500, regardless of income level. Note: It's essential to recognize that professional tax rates can change over time due to legislative amendments and state policies. To determine the specific rates applicable in your state, refer to the official website of your state's tax department or consult a tax professional knowledgeable about the current tax laws and rates in your region.Understanding the Mechanism of Professional Tax
Each state or union territory sets its own slab rates and formula for professional tax calculation. While the Indian Constitution grants exclusive power to Parliament for income tax laws (Union List), states can choose to levy professional tax (State and Concurrent Lists). This tax is deductible from taxable income and is a significant source of revenue for many Indian states and union territories. The Commercial Tax Department of each state is responsible for collecting professional tax.Who is Responsible for Collecting Professional Tax?
Employers are responsible for deducting and remitting professional tax on behalf of their employees. Self-employed individuals must register and pay this tax per the applicable slab rate. Some categories may be exempt based on state-specific criteria.Who is Responsible for Paying Professional Taxes
The responsibility for paying professional taxes in India is determined by the individual's or entity's circumstances, and it can vary based on their role and status:Employers
Regarding employees, the employer is responsible for deducting and remitting professional tax to the respective state government. However, this obligation is subject to any monetary threshold the state's legislation sets. Employers, including corporations, partnership firms, and sole proprietorships, who are also engaged in a trade or profession, must pay professional tax on their trade or profession. In such cases, employers must obtain a professional tax registration certificate for their trade or profession and a professional tax enrolment certificate to deduct the tax from their employee's salaries and remit it. Depending on the state's legislation, separate registrations may be necessary for each office or location.Self-Employed Individuals
Individuals engaged in freelancing or self-employment without employees must also register for professional tax, provided they meet the monetary threshold set by the respective state's legislation.Registration and Compliance for Professional Tax
Professional Tax Registration is a compulsory requirement that must be completed within 30 days of hiring employees for a business or, in the case of professionals, within 30 days from the commencement of their practice. To obtain the Registration Certificate, individuals and businesses must submit their application to the relevant state tax department within 30 days of hiring staff for their business operations. If the taxpayer operates from multiple locations, separate applications must be submitted to each relevant authority responsible for the respective workplace within their jurisdiction. [shortcode_57]Timelines for Professional Tax Payment
Meeting your Professional Tax obligations is essential, and the deadlines are contingent on your workforce size:- Employing Over 20 Employees: If you have more than 20 employees, prompt payment is crucial. You must remit your Professional Tax within 15 days from the close of the month.
- Employing Less than 20 Employees: Employers with fewer than 20 employees follow a quarterly payment schedule. This means you should submit your payment by the 15th of the following month at the end of each quarter.
Professional Tax Return Filing
Filing your Professional Tax Return is mandatory for all individuals and entities with Professional Tax Registration. However, the specific due dates for filing these returns can vary significantly from state to state. It's essential to stay updated with the regulations in your particular state to ensure timely compliance.Documents Needed for Professional Tax Registration
When applying for Professional Tax Registration, you will typically require the following documents and information:- For companies or Limited Liability Partnerships (LLPs), you must provide your Certificate of Incorporation or LLP Agreement as applicable.
- MOA (Memorandum of Association) and AOA (Articles of Association)
- PAN Cards of the Company, LLP, Proprietor, Owner, and Directors involved in the business.
- An NOC from the landlord is necessary if you lease the premises where the business operates.
- Passport-sized photographs of the Proprietor, Owner, and Directors involved in the business.
- Address and identity proof documents of the Proprietor, Owner, and Directors. This typically includes Aadhar card, Voter ID, Passport, etc.
- Information about your employees, including their names, addresses, and details of the salaries paid to them.
- Any other registrations or licenses related to your business, such as GST registration, Shop and Establishment License, etc., may be required, depending on your specific business activities and location.
Professional Tax Payment Method
Payment methods for professional tax may vary from state to state, and online and offline options are typically available through the respective state's official website.Professional Tax Payment Online
Many states provide an online platform for professional tax payment. To pay online, you should visit the official website of your state's tax department. There, you will likely find a dedicated section for professional tax payments. You must provide necessary details such as your registration number, PAN (if required), and the amount to be paid. Follow the instructions provided on the website to complete the payment securely.Professional Tax Payment Offline
In some cases, states may allow for offline payment methods. This typically involves visiting a designated government office or bank branch to submit your professional tax payment. You may need to complete a physical payment form and provide the necessary details for processing. The frequency of professional tax payments may vary by state. Some states require monthly payments, while others may have a quarterly or annual payment schedule. It's crucial to check your state's regulations to determine the correct payment frequency.Exemptions from Professional Tax
Professional tax is obligatory for most individuals earning a regular income, but specific exemptions are in place to alleviate the tax burden for specific categories of individuals. If you fall into any of the following categories, you are exempt from paying Tax:- Members of the Armed Forces: Individuals governed by the Army, Air Force, or Navy Act
- Persons with Disabilities: Individuals with mental or physical disabilities, such as blindness or deafness.
- Parents of Disabled Children: Parents of children suffering from disabilities also enjoy an exemption.
- Charitable Hospitals in Certain Areas: Charitable hospitals located in areas falling below the taluk level.
- Temporary Workers (Badli Workers): Temporary workers employed in a factory, known as "Badli Workers," are not required to pay.
- Operators of Educational Institutes: Individuals operating educational institutes are exempt from this tax.
- Foreign Nationals Employed by the State: Foreign individuals employed are exempted.
- Senior Citizens: Individuals aged 65 and above cannot pay.
- Women Engaged in Government's Mahila Pradhan Kshetriya Bachat Yojana: Women who are solely engaged as agents under the Government's Mahila Pradhan Kshetriya Bachat Yojana are exempted from this tax.
Consequences of Violating Professional Tax Regulations
The consequences for violating professional tax regulations can vary depending on the state's legislation. However, there are common penalties and consequences associated with non-compliance:- Late Registration: A penalty may be imposed if you fail to register for professional tax once it becomes applicable to you. The specific penalty amount can vary by state.
- Late Payment: Failing to make professional tax payments within the due date can lead to penalties. The penalty may be calculated based on a daily or monthly rate and can vary by state.
- Non-Payment or Delay: You may be penalized if you do not pay the professional tax or experience delays in payment. Sometimes, the penalty is a percentage of the tax amount owed.
- Late Return Filing: Many states require filing professional tax returns within specified due dates. Failure to file the return on time can result in penalties. The penalty amount may vary by state
- Late registration: Rs 5 per day.
- Late payment: 1.25% monthly interest on the overdue amount.
- Non-payment/delay of professional tax: A penalty of 10% on the tax amount.
- Late return submission: Penalties ranging from Rs. 1,000 to Rs. 2,000.
Difference Between TDS and Professional Tax
TDS (Tax Deducted at Source) and Professional Tax are distinct aspects of taxation in India, often confused due to their acronyms. Here's a clear differentiation:TDS (Tax Deducted at Source)
TDS is an amount deducted by your employer or the entity making payments to you, not by the individual receiving the income.- Applicability: It applies to various sources of income, such as salary, interest, rent, and professional fees, and is determined by pre-set TDS slabs.
- Control: Regulated by the national government (Income Tax Department).
- Who Pays: Deducted and paid by the entity making the payment on your behalf.
- Purpose: Ensures regular collection of income tax and minimizes tax evasion.
Professional Tax:
Professional tax is a direct tax paid by individuals or entities based on their profession, trade, or employment, and any other party does not deduct it.- Applicability: It is specific to professions, trades, and employment activities, with rates and rules varying by state.
- Control: Governed and managed by state governments.
- Who Pays: Paid directly by the individual or entity to the respective state government or deducted by employers from employees' salaries.
- Purpose: Generates state revenue for local development and infrastructure projects.
Simplify Your Professional Tax Registration with IndiaFilings
IndiaFilings can assist you with Professional Tax Registration in India. With our expertise and experience in business registration and compliance services, IndiaFilings can streamline the registration process, ensuring you meet all the requirements and submit accurate documentation. Our professional team can guide you through the application process, helping you save time and avoid potential pitfalls.Take the first step toward compliance today! Contact IndiaFilings for expert assistance.[shortcode_57]
Popular Post

In the digital age, the convenience of accessing important documents online has become a necessity...

The Atalji Janasnehi Kendra Project that has been launched by the Government of Karnataka...

The Indian Divorce Act governs divorce among the Christian couples in India. Divorce...

When an individual has more than a single PAN card, it may lead to that person being heavily penalised, or worse,...

Employees Provident Fund (PF) is social security and savings scheme for employee in India. Employers engaged...


