 Last updated: February 27th, 2023 4:36 PM
Last updated: February 27th, 2023 4:36 PM
What is the type of company in MCA?
The Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA) in India recognizes several types of companies under the Companies Act 2013. These companies are classified based on various factors, including ownership and control, liability, membership, formation, and Function. Understanding the different types of companies under the MCA is essential for entrepreneurs, investors, and other stakeholders. It helps them choose the proper company structure based on their needs and goals. The Companies Act 2013 also requires compliance with legal and regulatory requirements. The present article briefs the type of company in MCA.Classification of Companies
The Companies Act 2013 recognizes several types of companies, which can be classified into the following categories: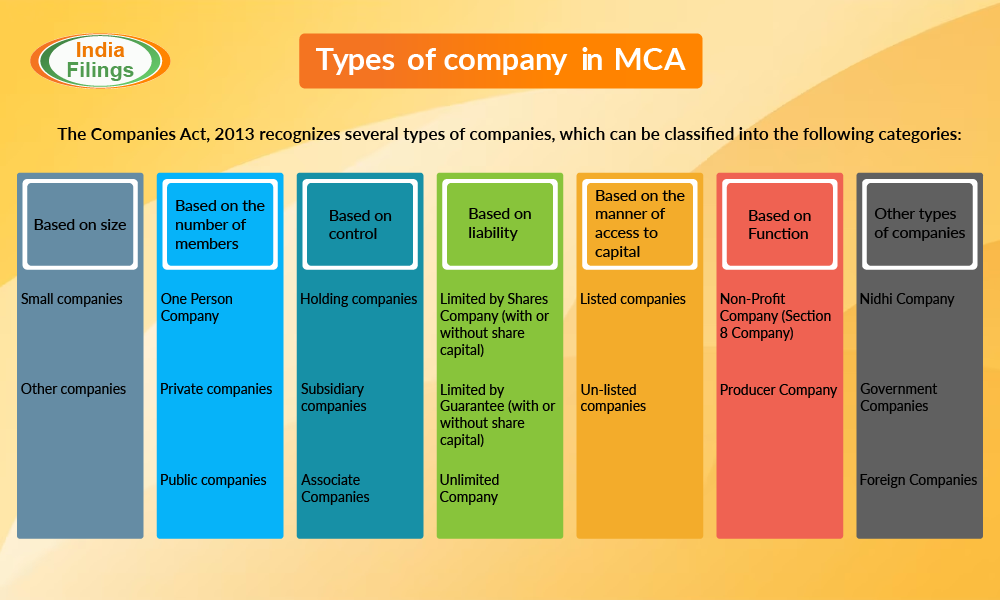 Type of company in MCA
Based on size:
Type of company in MCA
Based on size:
- Small companies
- Other companies
- One Person Company
- Private companies
- Public companies
- Holding companies
- Subsidiary companies
- Associate Companies
- Limited by Shares Company (with or without share capital)
- Limited by Guarantee (with or without share capital)
- Unlimited Company
- Listed companies
- Un-listed companies
- Non-Profit Company (Section 8 Company)
- Producer Company
Small companies
Small companies are defined as companies that have a paid-up share capital of up to 50 lakh rupees and a turnover of up to 2 Crores in the previous financial year.One Person Company
A one-person company (OPC) is a type of company that is owned and managed by a single person. OPC was introduced in 2013 to enable entrepreneurs to start a company without requiring a partner.Private companies
A private limited company is a type of company that has a minimum of two and a maximum of 200 shareholders. It has limited liability, which means that the shareholders are only liable to the extent of their share capital.Public companies
A public company is a type of company that has a minimum of seven shareholders and no maximum limit. It can raise capital from the public through the sale of shares, and its shares are traded on the stock exchange.Holding companies
A holding company holds a majority of the shares or controls the composition of the board of directors of another company. The company being held is referred to as the subsidiary of the holding company.Subsidiary company
A subsidiary company is a company that is controlled by another firm, known as the parent company or holding company. A subsidiary company can be wholly owned by the parent company or partly owned by other entities, including individuals or other companies.Associate Company
An associate company is defined as one in which another company has significant influence, but not control, over its management or financial policies.Limited by Shares Company
A company limited by shares is formed to conduct business and earn profits and is owned by shareholders who hold a certain number of shares in the company.Limited by Guarantee
A limited by Guarantee Company is a type of company in which the liability of the members is limited to the amount they have agreed to contribute in case the company is wound up. In other words, the company's members do not have any personal liability for the company's debts beyond the amount they have agreed to contribute.Unlimited company
An unlimited company is a type of company in which the liability of the members is not limited. The members are liable for all debts and obligations if the company is wound up.Listed companies
Listed companies refer to companies whose shares of stock are traded on a public stock exchange. These companies have met the stock exchange's listing requirements and have undergone a rigorous screening process before offering their shares to the public.Unlisted companies
Unlisted companies are private companies not listed on a public stock exchange. Small individuals or families usually own these companies, and their shares are not available for public trading.Non-Profit Company (Section 8 Company)
A section 8 non-profit company promotes commerce, art, science, sports, education, research, social welfare, religion, charity, and other similar objectives.Producer Company
A producer company is formed by ten or more producers (farmers, fishermen, handloom weavers, or any other producer) to improve their income, living standards, and production capacity.Other types of companies
Other companies, such as Nidhi Company, Government Companies, and Foreign Companies, are recognized under the Companies Act 2013.Popular Post

In the digital age, the convenience of accessing important documents online has become a necessity...

The Atalji Janasnehi Kendra Project that has been launched by the Government of Karnataka...

The Indian Divorce Act governs divorce among the Christian couples in India. Divorce...

When an individual has more than a single PAN card, it may lead to that person being heavily penalised, or worse,...

Employees Provident Fund (PF) is social security and savings scheme for employee in India. Employers engaged...


